Difference between revisions of "IS Families/IS256 family"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
====The IS''256'' cluster==== | ====The IS''256'' cluster==== | ||
| − | IS''256'' was first identified in 1987 as part of the [[wikipedia:Gentamicin|gentamycin]] resistance transposon Tn''4001''<ref><nowiki><pubmed>6323927</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref | + | IS''256'' was first identified in 1987 as part of the [[wikipedia:Gentamicin|gentamycin]] resistance transposon Tn''4001''<ref><nowiki><pubmed>6323927</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref name=":0"><pubmed>2833560</pubmed></nowiki></ref> from ''[[wikipedia:Staphylococcus_aureus|Staphylococcus aureus]]<ref name=":0" />''. It was observed that tandem duplication of IS''256'' contiguous with Tn''4001'' resulted in an increase in the level of resistance to [[wikipedia:Gentamicin|gentamycin]], [[wikipedia:Tobramycin|tobramycin]] and [[wikipedia:Kanamycin_A|kanamycin]] (Gm, Tm, and Km) implying the presence strong of IS''256''-associated promoters. Other examples of IS''256''-mediated increased gene expression have also been observed<ref><nowiki><pubmed>31474962</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>9371438</pubmed></nowiki></ref> IS''256'' is widely distributed in [[wikipedia:Staphylococcus|staphylococci]] and [[wikipedia:Enterococcus|enterococcus]]<ref><nowiki><pubmed>7899522</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>1334269</pubmed></nowiki></ref> where it is part of a variety composite transposons<ref><nowiki><pubmed>8654967</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>7625803</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>8031032</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>8723445</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. |
| − | Recently, a study of [https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-055018 ICE] elements identified examples from [[wikipedia:Group_B_streptococcal_infection|type B ''Streptococcus'']] [Tn''GBS''<ref | + | Recently, a study of [https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev-genet-112414-055018 ICE] elements identified examples from [[wikipedia:Group_B_streptococcal_infection|type B ''Streptococcus'']] [Tn''GBS''<ref name=":1"><pubmed>19183283</pubmed></nowiki></ref>] and ''[[wikipedia:Mycoplasma|Mycoplasma]]''<ref><nowiki><pubmed>23888872</pubmed></nowiki></ref> which include a DDE type Tpase rather than the more common phage integrase-like gene. Using a cascade [[wikipedia:BLAST_(biotechnology)|PSI-Blast]] approach not only revealed two new IS families (IS''Lre2'' and IS''Kra4'') but established a distant relationship with the IS''256'' and IS''H6'' families<ref name=":2"><pubmed>24418649</pubmed></nowiki></ref> ([[:File:Fig. IS256.1.png|Fig. IS256.1]] and [[:File:Fig. IS256.2.png|Fig. IS256.2]]). |
[[Image:Fig. IS256.1.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.1.''' Phylogenetic tree of prokaryotic Mutator-like transposases. Each p-MULT clade is colored according to figure 1. p-MULT 1 and p-MULT 2 transposases are encoded by ISs of the IS''256'' and IS''H6'' families, respectively. p-MULT 3 transposases are encoded by both the Tn''GBS'' family and the IS''Lre2'' family. p-MULT 4 encoded by both transposons and by ISs form three different lineages: IS''Azba1'', IS''Mich2'', and IS''Kra4''. Transposons of the IS''Azba1'' group encoding a pRiA4_Orf3-like protein are indicated by blue dots. IS of the IS''Mich2'' group with a predicted −1 frameshift in the transposase gene are indicated by pink dots. TE names are indicated at the extremity of the tree branches. TEs with a predicted σ<sub>A</sub> promoter at a distance of 13–17 bp from the IR-genome junctions in more than 20% of their insertion sites are indicated by small black dots.|alt=]] | [[Image:Fig. IS256.1.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.1.''' Phylogenetic tree of prokaryotic Mutator-like transposases. Each p-MULT clade is colored according to figure 1. p-MULT 1 and p-MULT 2 transposases are encoded by ISs of the IS''256'' and IS''H6'' families, respectively. p-MULT 3 transposases are encoded by both the Tn''GBS'' family and the IS''Lre2'' family. p-MULT 4 encoded by both transposons and by ISs form three different lineages: IS''Azba1'', IS''Mich2'', and IS''Kra4''. Transposons of the IS''Azba1'' group encoding a pRiA4_Orf3-like protein are indicated by blue dots. IS of the IS''Mich2'' group with a predicted −1 frameshift in the transposase gene are indicated by pink dots. TE names are indicated at the extremity of the tree branches. TEs with a predicted σ<sub>A</sub> promoter at a distance of 13–17 bp from the IR-genome junctions in more than 20% of their insertion sites are indicated by small black dots.|alt=]] | ||
[[Image:Fig. IS256.2.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.2.''' Alignment of the protein domains encompassing the catalytic DDE residues in p-MULT. Transposase sequences were aligned by the [https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/ MAFFT] alignment software and visualized using [https://www.jalview.org/ Jalview]. The alignment was filtered for redundancy to subsequently retain a subset of transposases for each p-MULT family representative of their diversity. Only regions surrounding the predicted DDE residues and the C/D(2)H motif were kept in the alignment. Numbers given in parentheses correspond to the distance in aa residues between the different motifs. Transposases accession numbers are indicated on the left.|alt=]] | [[Image:Fig. IS256.2.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.2.''' Alignment of the protein domains encompassing the catalytic DDE residues in p-MULT. Transposase sequences were aligned by the [https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/ MAFFT] alignment software and visualized using [https://www.jalview.org/ Jalview]. The alignment was filtered for redundancy to subsequently retain a subset of transposases for each p-MULT family representative of their diversity. Only regions surrounding the predicted DDE residues and the C/D(2)H motif were kept in the alignment. Numbers given in parentheses correspond to the distance in aa residues between the different motifs. Transposases accession numbers are indicated on the left.|alt=]] | ||
| − | Analysis of the N-terminal Tpase region<ref | + | Analysis of the N-terminal Tpase region<ref name=":2" /> also identified two shared domains (N1 and N2). N2 corresponds to a potential [[wikipedia:Helix-turn-helix|HTH domain]] in the region of the IS''256'' Tpase which recognizes the terminal IRs<ref name=":3"><pubmed>20543074</pubmed></nowiki></ref> ([[:File:Fig. IS256.3.png|Fig. IS256.3]]). |
| − | The cluster can be divided into five clades containing nine groups based on branching of the Tpases phylogenetic tree: two types of closely related Tn''GBS'', Tn''GBS1'' and Tn''GBS2'', and IS''Lre2'' (MULT3); the ''[[wikipedia:Mycoplasma|Mycoplasma]]'' ICE; IS''256'' (MULT1); IS''H6'' (MULT2); IS''Azba1'', IS''Mich2'', IS''Kra4'' (MULT4)<ref | + | The cluster can be divided into five clades containing nine groups based on branching of the Tpases phylogenetic tree: two types of closely related Tn''GBS'', Tn''GBS1'' and Tn''GBS2'', and IS''Lre2'' (MULT3); the ''[[wikipedia:Mycoplasma|Mycoplasma]]'' ICE; IS''256'' (MULT1); IS''H6'' (MULT2); IS''Azba1'', IS''Mich2'', IS''Kra4'' (MULT4)<ref name=":2" /> ([[:File:Fig. IS256.1.png|Fig. IS256.1]] and [[:File:Fig. IS256.2.png|Fig. IS256.2]] and [[:File:Fig. IS256.3.png|Fig. IS256.3]]). |
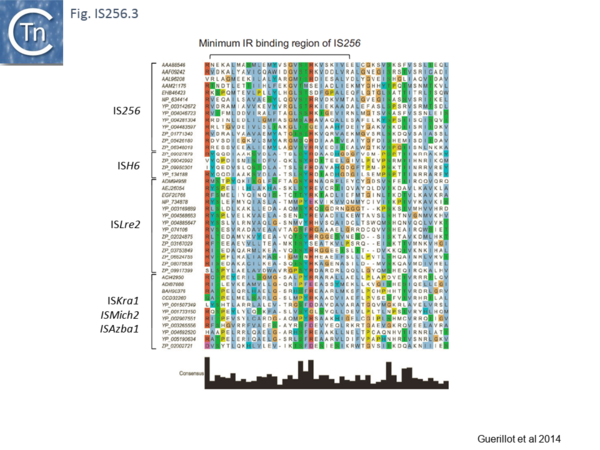
[[Image:Fig. IS256.3.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.3.''' Alignment of the predicted N-terminal DNA binding domain implicated in p-MULT IR recognition. Transposases identified in this study were aligned by the [https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/ MAFFT] alignment software and visualized using [https://www.jalview.org/ Jalview]. Only the predicted N2 domain encompassing the minimum IR-binding domain identified in the IS''256'' transposase (Hennig and Ziebuhr 2010) was retained in the alignment. The alignment was filtered for redundancy in order to keep a subset of transposases representative of the diversity of p-MULT 1, 2, 3, and 4 families. Transposases accession numbers are indicated on the left.|alt=]] | [[Image:Fig. IS256.3.png|thumb|center|600x600px|'''Fig. IS256.3.''' Alignment of the predicted N-terminal DNA binding domain implicated in p-MULT IR recognition. Transposases identified in this study were aligned by the [https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/ MAFFT] alignment software and visualized using [https://www.jalview.org/ Jalview]. Only the predicted N2 domain encompassing the minimum IR-binding domain identified in the IS''256'' transposase (Hennig and Ziebuhr 2010) was retained in the alignment. The alignment was filtered for redundancy in order to keep a subset of transposases representative of the diversity of p-MULT 1, 2, 3, and 4 families. Transposases accession numbers are indicated on the left.|alt=]] | ||
| − | There is a distant relationship with the Tpase of the eukaryotic Mutator TE and, like MuDR from ''[[wikipedia:Maize|Zea mays]]'', many generate 8-9-bp target repeat on insertion. They have therefore been called MULE (for '''Mu'''tator-'''L'''ike '''E'''lements). Like MuDr/Foldback, members of these groups carry a largely α-helical insertion domain between the second D and E catalytic residues. This includes a conserved C/D(2)H signature present in the eukaryotic and prokaryotic IS<ref | + | There is a distant relationship with the Tpase of the eukaryotic Mutator TE and, like MuDR from ''[[wikipedia:Maize|Zea mays]]'', many generate 8-9-bp target repeat on insertion. They have therefore been called MULE (for '''Mu'''tator-'''L'''ike '''E'''lements). Like MuDr/Foldback, members of these groups carry a largely α-helical insertion domain between the second D and E catalytic residues. This includes a conserved C/D(2)H signature present in the eukaryotic and prokaryotic IS<ref name=":2" /><ref><nowiki><pubmed>21518873</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. |
====IS''256''==== | ====IS''256''==== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
=====IS''256'' group===== | =====IS''256'' group===== | ||
| − | The classical IS''256'' group has large number of members in both bacteria and archaea. They are between 1200 and 1500 bp long with IR of 20-30 bp ([[:File:Fig. IS256.4.png|Fig. IS256.4]]) and generate DR of between 8 and 9 bp. A single long orf carrying a potential DDE motif with a spacing of 112 residues between the second D and E residues ([[:File:Fig. IS256.2.png|Fig. IS256.2]]), together with a correctly placed K/R residue. This spacing is due to an insertion domain<ref><nowiki><pubmed>20067338</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>23217365</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. The catalytic residues have been validated by mutagenesis<ref | + | The classical IS''256'' group has large number of members in both bacteria and archaea. They are between 1200 and 1500 bp long with IR of 20-30 bp ([[:File:Fig. IS256.4.png|Fig. IS256.4]]) and generate DR of between 8 and 9 bp. A single long orf carrying a potential DDE motif with a spacing of 112 residues between the second D and E residues ([[:File:Fig. IS256.2.png|Fig. IS256.2]]), together with a correctly placed K/R residue. This spacing is due to an insertion domain<ref><nowiki><pubmed>20067338</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>23217365</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. The catalytic residues have been validated by mutagenesis<ref name=":4"><pubmed>12169594</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. It was shown several years ago that the Tpase of IS''256'' family elements share some similarities with the eukaryotic Mutator element<ref><nowiki><pubmed>8041625</pubmed></nowiki></ref>, a relationship which has been explored recently in more detail<ref><nowiki><pubmed>19018586</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. |
| − | Members of this family transpose using an excised circular dsDNA transposon intermediate [e.g. <ref | + | Members of this family transpose using an excised circular dsDNA transposon intermediate [e.g. <ref name=":4" /><ref name=":5"><pubmed>11751820</pubmed></nowiki></ref>]. They are also found as part of composite transposons such as Tn''4001'' flanked on either side by IS''256''<ref><nowiki><pubmed>6323927</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref name=":0" /><ref><nowiki><pubmed>2553542</pubmed></nowiki></ref><ref><nowiki><pubmed>2544565</pubmed></nowiki></ref>. For IS''256'' itself, the sequences of circle junctions showed that the left IS end preferentially attacked the right end<ref name=":5" />, a result that was independently demonstrated by the effect of small deletions in the left and right ends on circle formation<ref name=":3" />. |
=====IS''1249'' group===== | =====IS''1249'' group===== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
====IS''Lre2''==== | ====IS''Lre2''==== | ||
| − | There are 48 entries for ISLre2 family members in [https://isfinder.biotoul.fr/ ISfinder]. They are restricted at present to the bacteria. They are between 1500 and 2000 bp long, with IR from 15 to 29 bp ([[:File:Fig. IS256.5.png|Fig. IS256.5]]) and generate 9 bp DR. Together with the related TnGBS ICE, show strong target specificity and insert 13-17 bp upstream of σA promoters<ref | + | There are 48 entries for ISLre2 family members in [https://isfinder.biotoul.fr/ ISfinder]. They are restricted at present to the bacteria. They are between 1500 and 2000 bp long, with IR from 15 to 29 bp ([[:File:Fig. IS256.5.png|Fig. IS256.5]]) and generate 9 bp DR. Together with the related TnGBS ICE, show strong target specificity and insert 13-17 bp upstream of σA promoters <ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /> in oriented fashion with RE proximal. PCR analysis has detected a transposon circle junction, as with the related ICE, suggesting that transposition may occur via a Donor Primed Transposon Replication process. |
====IS''Kra4''==== | ====IS''Kra4''==== | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 22 June 2020
Contents
The IS256 cluster
IS256 was first identified in 1987 as part of the gentamycin resistance transposon Tn4001[1][2] from Staphylococcus aureus[2]. It was observed that tandem duplication of IS256 contiguous with Tn4001 resulted in an increase in the level of resistance to gentamycin, tobramycin and kanamycin (Gm, Tm, and Km) implying the presence strong of IS256-associated promoters. Other examples of IS256-mediated increased gene expression have also been observed[3][4] IS256 is widely distributed in staphylococci and enterococcus[5][6] where it is part of a variety composite transposons[7][8][9][10].
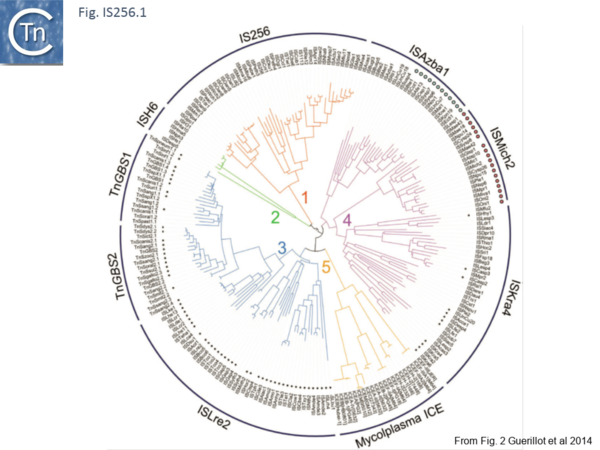
Recently, a study of ICE elements identified examples from type B Streptococcus [TnGBS[11]] and Mycoplasma[12] which include a DDE type Tpase rather than the more common phage integrase-like gene. Using a cascade PSI-Blast approach not only revealed two new IS families (ISLre2 and ISKra4) but established a distant relationship with the IS256 and ISH6 families[13] (Fig. IS256.1 and Fig. IS256.2).

Analysis of the N-terminal Tpase region[13] also identified two shared domains (N1 and N2). N2 corresponds to a potential HTH domain in the region of the IS256 Tpase which recognizes the terminal IRs[14] (Fig. IS256.3).
The cluster can be divided into five clades containing nine groups based on branching of the Tpases phylogenetic tree: two types of closely related TnGBS, TnGBS1 and TnGBS2, and ISLre2 (MULT3); the Mycoplasma ICE; IS256 (MULT1); ISH6 (MULT2); ISAzba1, ISMich2, ISKra4 (MULT4)[13] (Fig. IS256.1 and Fig. IS256.2 and Fig. IS256.3).
There is a distant relationship with the Tpase of the eukaryotic Mutator TE and, like MuDR from Zea mays, many generate 8-9-bp target repeat on insertion. They have therefore been called MULE (for Mutator-Like Elements). Like MuDr/Foldback, members of these groups carry a largely α-helical insertion domain between the second D and E catalytic residues. This includes a conserved C/D(2)H signature present in the eukaryotic and prokaryotic IS[13][15].
IS256
The IS256 family can be subdivided into 3 groups: IS256, IS1249, and ISC1250.
IS256 group
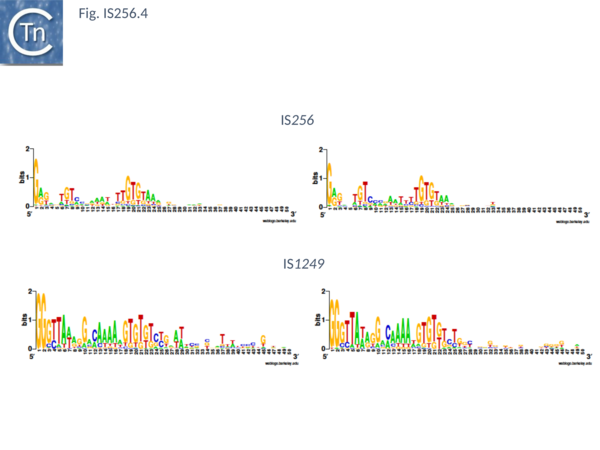
The classical IS256 group has large number of members in both bacteria and archaea. They are between 1200 and 1500 bp long with IR of 20-30 bp (Fig. IS256.4) and generate DR of between 8 and 9 bp. A single long orf carrying a potential DDE motif with a spacing of 112 residues between the second D and E residues (Fig. IS256.2), together with a correctly placed K/R residue. This spacing is due to an insertion domain[16][17]. The catalytic residues have been validated by mutagenesis[18]. It was shown several years ago that the Tpase of IS256 family elements share some similarities with the eukaryotic Mutator element[19], a relationship which has been explored recently in more detail[20].
Members of this family transpose using an excised circular dsDNA transposon intermediate [e.g. [18][21]]. They are also found as part of composite transposons such as Tn4001 flanked on either side by IS256[22][2][23][24]. For IS256 itself, the sequences of circle junctions showed that the left IS end preferentially attacked the right end[21], a result that was independently demonstrated by the effect of small deletions in the left and right ends on circle formation[14].
IS1249 group
There are more than 30 members confined at present to the Actinobacteria and the Firmicutes. They are about 1300 pb in length with IR of about 26bp (Fig. IS256.4) and generally generate DR of 8bp (with variations of between 0 and 10).
ISC1250 group
At present, there are only 3 members of this group in ISfinder. All are found in the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus.
ISH6
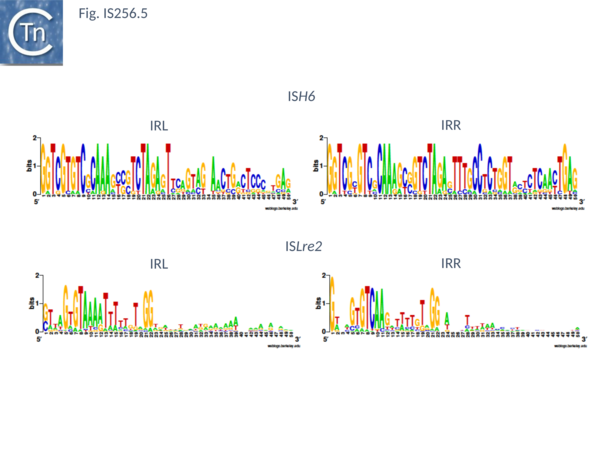
This group (MULT2) were originally observed uniquely in archaea[25]. There are 11 members of about 1450 bp with highly conserved IR of 24-27bp (Fig. IS256.5), DR of 8 bp and a single Tpase orf encoding a protein of 450 bp.
ISLre2
There are 48 entries for ISLre2 family members in ISfinder. They are restricted at present to the bacteria. They are between 1500 and 2000 bp long, with IR from 15 to 29 bp (Fig. IS256.5) and generate 9 bp DR. Together with the related TnGBS ICE, show strong target specificity and insert 13-17 bp upstream of σA promoters [11][13] in oriented fashion with RE proximal. PCR analysis has detected a transposon circle junction, as with the related ICE, suggesting that transposition may occur via a Donor Primed Transposon Replication process.
ISKra4
This newly emerging family includes 83 members and is divided into three related groups: ISAzba1, ISMich2 and ISKra4.
ISAzba1
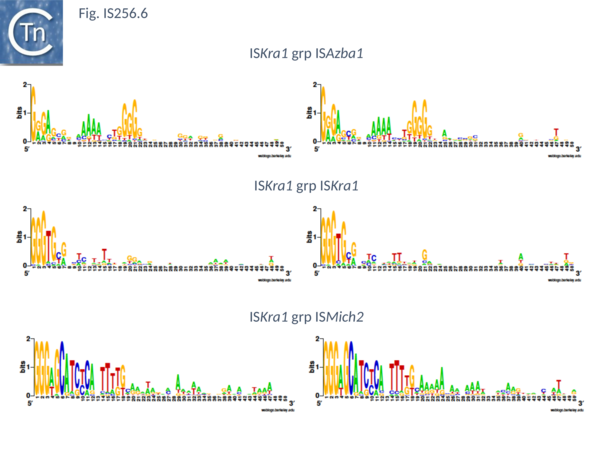
There are presently 28 members of this group. They encode a Tpase of between 450 and 480 aa, are 1400 to 2900 bp long with IR of about 20 bp (Fig. IS256.6) and no DR. Six (ISAfe13, ISCot1, ISEc51, ISKpn19, ISSysp7) carry an orf in addition to the Tpase and this specifies a protein related to serine-recombinases or resolvases. Four of these also include a third orf annotated as hypothetical protein. The fifth, ISAfe13, carries the Tpase, a resolvase, and an alternative orf annotated as ORF-3-like from plasmid pRiA4b. Other proteins found in this family are annotated as being hypothetical or putative TnpR resolvases although no direct evidence for resolvase function is available. Eight other members simply encode the Tpase and the ORF-3 like protein. While ISCep1 includes the ORF-3-like protein and a third annotated as phage integrase or xerC/D.
ISMich2
This includes 24 members which are presently limited to the cyanobacteria. Twenty two have a Tpase orf distributed between two reading phases while in the remaining 2 the Tpase forms a unique continuous orf. However all show a potential but atypical frameshift motif, TTTTTT which could be involved in either PRF (Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting) or PTR (Programmed Transcriptional Frameshifting) recoding. The further experimental analysis would be necessary to confirm or refute this. Members are between 1250 and 1400 bp long with a Tpase of 360aa, IR of between 18 and 39 bp (Fig. IS256.6) with 8 bp DR. Three members (ISCysp26; ISMic1; ISMich2) carry a passenger gene annotated as hypothetical protein.
ISKra4
This small group of elements range in size from 1400 to 3700 pb due to the presence in some of various passenger genes. They have IR of 18 to 31 bp (Fig. IS256.6) and generate DR of 9 bp. Three carry passenger genes: ISLdr1, a hypothetical protein and a reverse transcriptase; ISSri1, a transcriptional regulator; and ISTn1, a hypothetical protein. Six members may express their Tpases by frameshifting (5 include a 7A motif and 1 with a motif, 5TC).
Bibliography
- ↑ <pubmed>6323927</pubmed>
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Lyon BR, Gillespie MT, Skurray RA . Detection and characterization of IS256, an insertion sequence in Staphylococcus aureus. - J Gen Microbiol: 1987 Nov, 133(11);3031-8 [PubMed:2833560] [DOI] </nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>31474962</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>9371438</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7899522</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>1334269</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8654967</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>7625803</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8031032</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>8723445</pubmed>
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 </nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>23888872</pubmed>
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 </nowiki>
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 </nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>21518873</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>20067338</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>23217365</pubmed>
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Loessner I, Dietrich K, Dittrich D, Hacker J, Ziebuhr W . Transposase-dependent formation of circular IS256 derivatives in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. - J Bacteriol: 2002 Sep, 184(17);4709-14 [PubMed:12169594] [DOI] </nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>8041625</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>19018586</pubmed>
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 </nowiki>
- ↑ <pubmed>6323927</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2553542</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>2544565</pubmed>
- ↑ <pubmed>17347521</pubmed>